Beijing: 1# Chaoqian Road, Science Park, Changping District, Beijing, China
Shanxi: 5-1#, Zone 2, 69 JinXiu Avenue, YangQu, Taiyuan, Shanxi, China
North Region: +86-10-18515571376
South Region: +86-10-18515571396
Applications of CO2 Laser in the Medical and Pharmaceutical Industry
Traceability of medical products and pharmaceuticals is of paramount importance in the healthcare sector, as it enables the tracking and isolation of defective or contaminated drugs, significantly aiding regulatory compliance. CO2 lasers can permanently mark information onto pharmaceutical packaging materials, including cards, foils, plastics, and glass.

1. Marking Glass Vials:
CO2 lasers mark glass by creating microscopic cracks on the surface of the material. The textures produced by CO2 lasers can replicate a sandblasted effect, making them suitable for marking cosmetic and perfume bottles, as well as cups and crystal glassware.

2. Marking Pharmaceutical Packaging:
Many medications and drugs are packaged in cardboard boxes, which require a range of information for traceability. CO2 lasers can ablate the ink coating on the cardboard, resulting in high-quality and easily recognizable markings. Information such as production dates, batch codes, barcodes, and QR codes can be dynamically applied on the production line and updated as needed.

3. Marking Plastic Packaging:
CO2 lasers are capable of marking a variety of plastic products, including packaging films and plastic bottles. The appearance of the markings largely depends on the type of plastic used. In many cases, CO2 lasers do not cause a change in color of the plastic; however, special additives can be employed when more pronounced, high-contrast markings are required. Additionally, CO2 lasers can be utilized to perforate silicone nipples for baby bottles.

4. Marking the Surface of Pharmaceuticals:
CO2 lasers can perforate the surface of tablets to regulate drug release. By creating one or more small holes in rigid tablets with a semi-permeable outer membrane, the active ingredients are absorbed by the body as the tablet enters. During the manufacturing process, CO2 lasers can be integrated with a vision system to provide greater flexibility and control over the size, depth, and shape of the perforations.

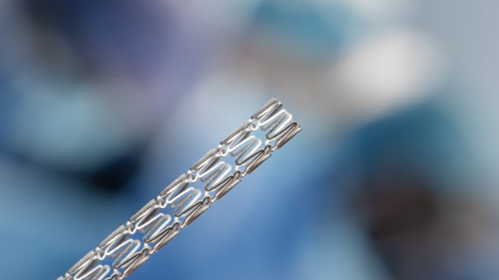
5. Stent Cutting:
Stents are small tubular frameworks placed within blocked blood vessels or catheters to maintain the smooth flow of blood or fluids. Coronary stents and vascular stents are used within arteries, while other types may be employed in the bile duct, urinary tract, colon, and esophagus. Depending on their application, stents can be made from materials such as plastics (including polyethylene, polyurethane, and Teflon) or metals (such as stainless steel, nickel-titanium alloy, or platinum).
Laser cutting is an ideal choice for the manufacturing process of stents. Any minor defect in a stent can have significant implications for patient safety; thus, laser cutting allows for precise and consistent detailed processing, ensuring uniformity in shape and size. The entire process can be automated, ensuring efficiency and speed. Laser equipment can handle a variety of materials while consistently meeting stringent quality standards, making it the preferred method in the industry.
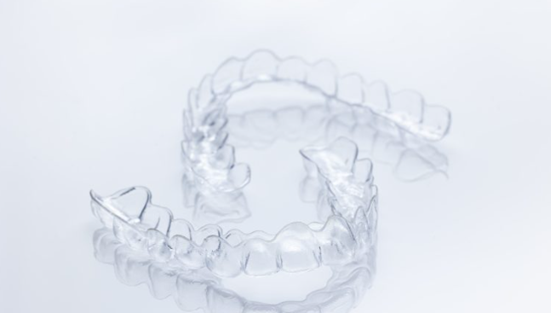
6. Orthodontic Aligner Cutting:
Invisible dental aligners are gradually replacing traditional metal braces. Each aligner is typically worn for about two weeks. With an average treatment duration exceeding one year, each patient usually requires at least 30 aligners to achieve the desired correction. In the early stages of aligner technology, production relied heavily on manual craftsmanship. Today, the application of laser cutting technology has significantly reduced manufacturing time and costs while greatly enhancing quality and consistency.
Invisible aligners are made from various transparent thermoplastic polymer materials, including medical-grade polyurethane, PET, and polypropylene. These materials exhibit excellent absorption of the CO2 laser wavelength, making CO2 lasers particularly suitable for cutting aligners. In this application, smooth and high-quality cuts are crucial, as they minimize the need for subsequent manual adjustments and prevent any flaws that could cause discomfort for the patient.