Beijing: 1# Chaoqian Road, Science Park, Changping District, Beijing, China
Shanxi: 5-1#, Zone 2, 69 JinXiu Avenue, YangQu, Taiyuan, Shanxi, China
North Region: +86-10-18515571376
South Region: +86-10-18515571396
13.1 Check the power supply
1. Check whether the power supply wiring is normal.
2. Confirm the power supply specification. For details, see [Attachment: CO2 Laser Power Supply and Water Cooler Configuration Table].
3. Measure whether the power supply has normal output.
13.2 Check the control system
1. Check and confirm whether the signal cable is properly connected.
2. Confirm whether the controller outputs PWM signals.
3. Use a voltmeter to detect whether there is a 0-5V output voltage between PWM and GND when a signal is given.
13.3 Check the cooling system (Water- cooled laser sources)
1. Confirm the specifications of the chiller. For details, see [Attachment: CO2 Laser Power Supply and Chiller Configuration Table]
2. Ensure that the pipeline connection for the chiller is normal and the water flow is unobstructed. When the chiller is not switch on, a rise in temperature inside the chamber can trigger the laser's overheat protection program and potentially affect its performance.
Please ensure proper water usage. It is recommended to add a water protection wiring to the lasers. The specific wiring method is as follows:
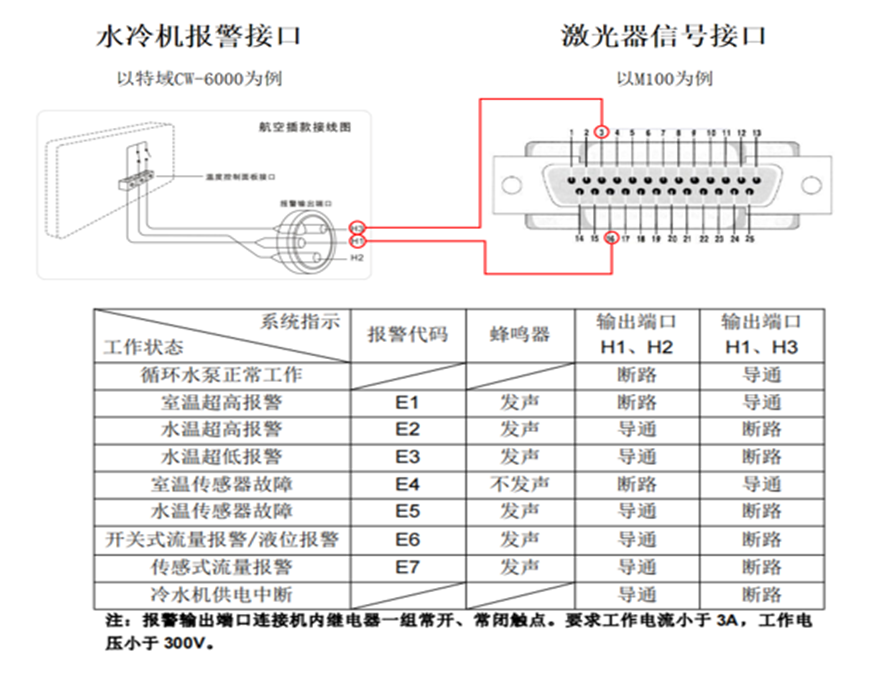
13.4 Lasers protect program(M series laser sources)
To prevent the laser circuit board chips from being burned due to immediately signal emission after the laser is powered on, DAVI LASER has loaded a protection program that allows normal control of beam emission only after the lasers has been powered on for 1 minute.
Phenomenon: The lasers suddenly stopped emitting beam after working for a period of time, but it returned to normal if restarted.
14.1 Laser overheats protection (Air- cooled laser sources)
Due to the ambient temperature is too high, the lasers have been working under the condition of near-full duty cycle for a long time, under poor cooling conditions, and excessive dust on-site that cause dust accumulation on the lasers fan and heat sink, or chassis enclosure with poor air circulation, all these factors could degrade the cooling effect of the lasers, resulting in higher temperature, therefore triggering the laser's overheat protection program.
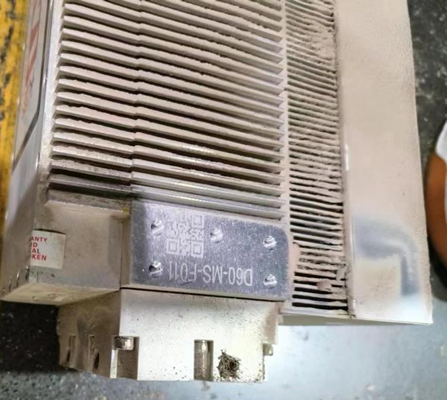 Picture 1: A laser source which dust covers the heat sink
Picture 1: A laser source which dust covers the heat sink
14.2 Power supply issue
It may due to unstable voltage. It is recommended to check the stability of the 220V AC input and 48V DC output of the laser power supply. A multi-meter can be used to measure the voltage changes of input and output while the lasers has encountered an abnormal situation. Either replace the 220V AC power supply cable or replace the power supply to test if the abnormality still occurs.
14.3 The chiller(Water-cooled laser sources)
1. Insufficient cooling capacity.
2. The water pipe is too long. Try to shorten it, generally not exceeding 2m.
3. The water pressure is too low and is not within the required range.
14.4 Cooling water(Water-cooled laser sources)
1. The cooling water level in the chiller is below the standard line;
2. The cooling water is not deionized or distilled, cause accumulation of scale inside the water-cooled laser source, which reduces the water flow rate and cooling effect, and in severe cases, may cause the water-cooled laser source to rupture.
15.1 Beam path
1. The components on the beam path block the laser beam;
2. The lenses on the beam path are contaminated or damaged;
Picture 2: Broken lens of the beam expander
3. The transmittance of the optical lens used to the 10.6/10.2/9.3 μ m wavelength is low;
4. The laser type is not suitable for application. The beam path is too long but if choose a laser source with low power ,it cannot meet the requirements.
15.2 lenses of the laser source
1. Output mirror contamination
 Picture 3: Output lens burned due to contamination
Picture 3: Output lens burned due to contamination
2. The processed material exhibits high reflectivity to laser beam of 10.6um wavelength , cause the internal reflector of the laser source burned.
 Picture 4: Internal reflective lens burned by reflected laser beam
Picture 4: Internal reflective lens burned by reflected laser beam
15.3 Heat dissipation
Poor heat dissipation of the lasers cause increased temperature, which results in a decrease in power output.
15.4 Laser Gas
The laser has been in use for a long time and CO2 gas is loss, resulting in power drop.
16.1 The lasers not ready for working
This situation usually occurs during the step of start-up. The reason is the ambient temperature is low or the lasers is not used for a long time, resulting in a long preparation (periodization)time of the laser source.
The solution is as follows: Recover the laser source temperature to workshop temperature, preheat the laser source with 1% power for 5-10 minutes after 30s of start-up, and then increase the power gradually after laser beam emitting.
16.2 The circuit is damaged
It is necessary to wait for the laser source completely warm-up after switching on. Once it is ready, it can be applied to emit laser beam.
In the case of the operation is not conducted as per the preheat procedure and immediately get the lasers working with high power after switching on, it would easily result in the circuit chips to burn out.
16.3 Laser Gas leakage
1. Due to dust prevention measures were not taken properly, or the influence of other burned lenses on the beam path, cause the output mirror becomes contaminated and burned through, internal gas leakage. It often accompanied by phenomena such as cavity contamination and circuit chip burnout.
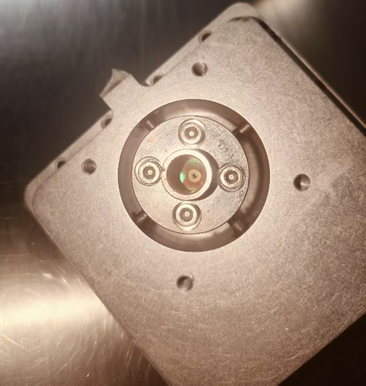 Picture 5: The output mirror which is burned through due to contaminated
Picture 5: The output mirror which is burned through due to contaminated
2. The front and rear end plates of the laser source were on impacted, causing the components to loosen and resulting in internal gas leakage.
Question 17: Beam mode quality becomes poor
17.1 Screw loose
The beam shaping mirror (M100/M150 and M2-100/M2-150 laser sources) is displaced or rotated due to screw looseness. Generally, the reasons are as follows:
1. Disassemble without permission.
2. The shaping mirror is impacted.
3. Hold the laser shaping barrel in one’s hand while moving the laser source.
 Picture 6: Prohibited to move the laser source with the barrel of the beam shaping mirror
Picture 6: Prohibited to move the laser source with the barrel of the beam shaping mirror
17.2 Manually rotate the dimming screw
The effect of beam spot becomes poor, the power drops as well.
1. Ensure proper grounding to prevent signal interference, which could cause the power unstable.
2. For switching power supplies, it is advised to choose single-module power supplies that meet the requirements, to avoid lasers faulty caused by the use of multiple power supplies connected in parallel or in series.
3. When the laser source is being used again after not working for a long time, it is necessary to preheat ( warm-up) it with lower power (1%-2%) for 5-10 minutes. After confirming that the laser source has power output, run it under the 5% of duty cycle for 5 minutes, and then gradually increase the power.
4. Check and clean the surface of the laser source regularly.
5. Pay attention to the dust protection for the laser output mirror and check the condition of the mirror regularly.
6. Control of water temperature: The setting of water temperature should be based on the temperature and humidity of the environment to prevent condensation due to excessive temperature differences, which could damage the circuit and window mirror. If conditions permit, water shut-off protection is needed. Deionized water or distilled water should be used as circulating water.
